Glycolysis is the central pathway for the glucose catabolism in which glucose 6-carbon compound is converted into pyruvate 3-carbon compound through a sequence of 10 steps. Isomerization of Glucose-6-Phsphate to Fructose-6-Phosphate.

Solved During Glycolysis Isomerization Occurs During Which Chegg Com
The overall reaction of glycolysis which occurs in the cytoplasm is.

. In glycolysis a six-carbon sugar known as glucose is split into two molecules of a three-carbon sugar called pyruvate. C- Glucose glucose 6-phosphate. Two three-carbon molecules are converted into two molecules of pyruvate as four molecules of ATP are produced.
Beta-oxidation of fatty acids and during the citric acid cycle. Glycolysis which translates to splitting sugars is the process of releasing energy within sugars. Indeed this enzyme like all other enzymes is able to catalyze the reaction in both directions.
During which of the following steps of Glycolysis Phosphorylation does not occur. C 6 H 12 O 6 2 NAD 2 ADP 2 P ----- 2 pyruvic acid CH 3 COCOOH 2 ATP 2 NADH 2 H. There are two energy-conserving reactions of the process of glycolysis where step 06 is the first of them and step 09 is the second of them.
Glucose 6- phosphate fructose 6- phosphate d. This reaction requires energy and so it is coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and Pi. NAD is the oxidizing agent in glycolysis as it is in most other energy yielding metabolic reactions eg.
6 During glycolysis isomerization occurs during which of the following reactions. In step 06 13-bisphosphoglycerate is formed from Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. At this time concentrate on the fact that glucose with six carbons is converted into two pyruvic acid molecules with three carbons each.
The glycolytic sequence of reactions differs from one. This multistep process yields two ATP molecules containing free energy two pyruvate molecules two high energy electron-carrying molecules of NADH. Fructose 16-bisphosphate dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate Fructose 6-phosphate fructose 16- bisphosphate Glucose 6-phosphate fructose 6- phosphate D Glucose glucose 6-phosphate.
In chemistry and physics matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. Fructose 6-phosphate fructose 16-bisphosphate c. The sixth and seventh reactions of glycolysis are as a whole an energy-coupling process.
During glycolysis isomerization occurs during which of the following reactions. Glycos sugar and lysis breaking or dissolution the splitting up of sugar. D- Fructose 16-bisphosphate dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
In this oxidation is in the form of release of hydrogen which reduces NAD to NADH2. The phosphate group from ATP is joined to the glucose molecule by an enzyme known as hexokinase. Glycolysis is a primary step of cellular respiration.
Aerobic glycolysis occurs when oxygen is sufficient. Classification and Properties of Matter. All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of atoms which are made up of interacting subatomic particles and in everyday as well as scientific usage matter generally includes atoms and anything made up.
During glycolysis isomerization occurs during which of the following reactions. B- Glucose 6-phosphate fructose 6- phosphate. A Fructose 16-bisphosphate dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
Thus once glucose enters the cell it gets phosphorylated. Glycolysis 2 Step-wise reactions of glycolysis Reaction 1. During this reaction NAD is reduced and NADH is generated by.
A- Fructose 6-phosphate fructose 16- bisphosphate. Phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6 phosphate. During glycolysis isomerization occurs during which of the following reactions.
Oxidative Phosphorylation of Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate. It has a low Km for glucose.
During glycolysis the glucose molecule is converted to Glucose-6-phosphate as a result of phosphorylation. During glycolysis isomerization occurs during which of the following reactions. 1 Conversion of Glucose to Glucose-6-P 2 Conversion of Glucose-6-P to Fructose-6-P 3 Conversion of Fructose-6-P to Fructose 16 bisphoshate 4 Both A and C Respiration in Plants Botany Practice questions MCQs Past Year Questions PYQs NCERT Questions Question.
First glucose is converted into pyruvate and then pyruvate will be oxidized to the final products CO2 and H2O. In it oxidation of glucose is involved. During glycolysis one glucose molecule makes two molecules of pyruvate.
Conversion of 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde to 13- biphosphoglycerate is an oxidation reaction. This step is irreversible. Glycolysis is the series or sequence of reactions or pathways by which glucose is broken down anaerobically to form pyruvic acid.
The free energy released in this process is used to. B Fructose 6-phosphate fructose 16-bisphosphate. And the direction leading to the synthesis of 13-bisphosphoglycerate occurs during the photosynthetic CO 2 fixation and gluconeogenesis.
Fructose 16-bisphosphate dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehydes 3- phosphate b. The NADH thus produced is primarily used to ultimately transfer electrons to O 2 to produce water or when O 2 is not available to produced compounds such as lactate or ethanol see Anoxic regeneration of. Steps of Glycolysis process 06.
Oxidation of organic substrate occurs in glycolysis for the release of energy. It is an energy-yielding reaction. Glycolysis takes place in both aerobic and anaerobic organisms and is the first step towards the metabolism of glucose.
A Fructose 16-bisphosphate dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate B Fructose 6-phosphate fructose 16- bisphosphate C Glucose 6- phosphate fructose 6- phosphate D Glucose glucose 6- phosphate Answer.

Solved 4 Which Of The Following Reactions Is A Driving Chegg Com

Glycolysis Biology For Majors I
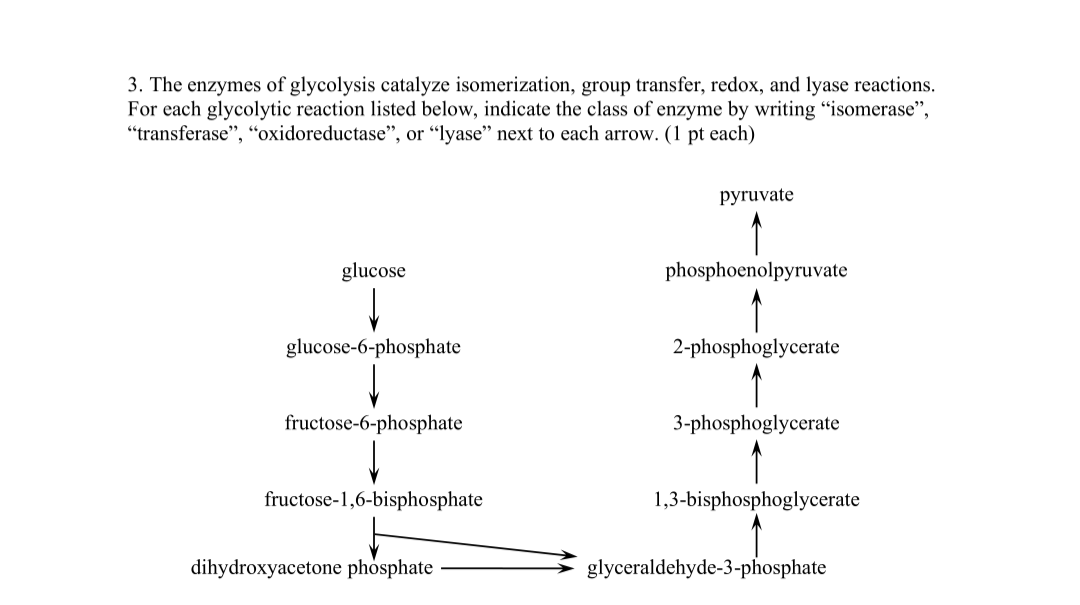
Solved 3 The Enzymes Of Glycolysis Catalyze Isomerization Chegg Com

0 Comments